Identification of Need for 2 Apparent Horizons:
The goal of this research is to develop the ability to find two apparent
horizons around two distinct
black holes. When evolving a spacetime, two coalescing black
holes will go from having two distinct
horizons to one horizon. The apparent horizon finders are utilized
at foliation to find the horizon(s).
The following snapshots of ser data show the ability of the
curvature flow method to identify the
need for two horizons. The initial surface is a user specified
2-sphere. The flow of the surface
is controlled by the outgoing expansion of the curvature. The
flow of the surface makes up a set
of levels for which the expansion is a constant all along the surface
at teat instant. By tracking these
levels, the need to break into two surfaces is identified. The
identification uses the gradient of the
expansion along the levels. To ensure the correct choice is made,
an additional criterion is any
spikes occurring in the expansion of the curvature. With both
of these criteria the need to break into
two horizons is demonstrated.
The following snapshots are grouped in fours. The nomenclature
is (x,z) pairs with the y set to 0.
For example, x0z.5 means (0,.5M), indicating that the holes are located
at (0,.5M) and (0,-.5M)
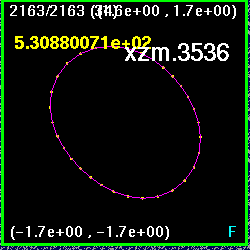
where M=1. Also, xz.3536 for example, indicates (0.3536,0.3536)
and (-0.3536,-0.3536) location
for the holes while xzm.3536 indicates the minus of this (-0.3536,0.3536)
and (0.3536,-0.3536).
Separation of holes = 1.0, no need for breaking detected. These ran
until H=0.001.
Now all four snapshots are orientated and merged together. The
lines are color coded such that
x0z.5 is purple, xz.707 is white, xzm.707 is blue, and x.5z0
is orange. The largest
discrepancy is in the x0z.5, in other words the black holes are at
(0,0.5) and (0,-0.5).
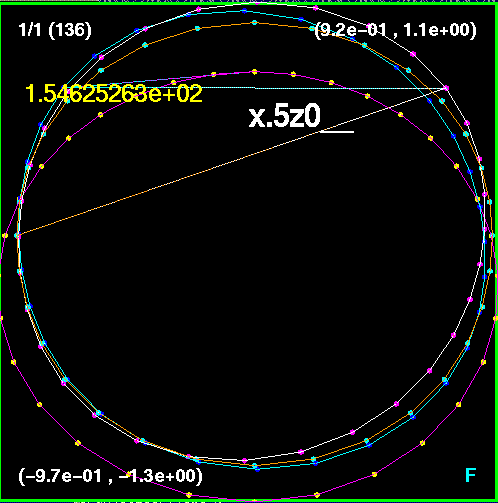
Separation of holes = 1.53, the on x-axis and z-axis data concurs with
the critical separation of 1.53
established by Cadez, A. in 1974 (Ann. Phys., NY 83, 449-457).
One problem remains,
the off-axis figures indicating breaking when set to 0.54, a smaller setting
was needed.
Work is in progress to understand this problem.
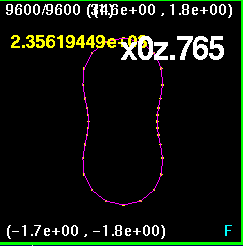
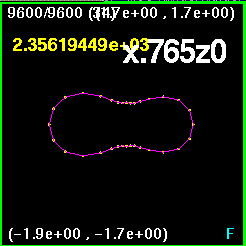
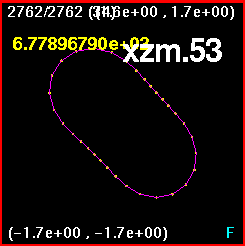
Now all four snapshots are orientated and merged together. The
lines are color coded such that
x0z.765 is purple, xz.53 is white, xzm.53 is blue, and x.765z0
is orange. Clearly, the largest
discrepancy is in the x.765z0. in other words the black holes are at
(0.765,0) and (-0.765,0).
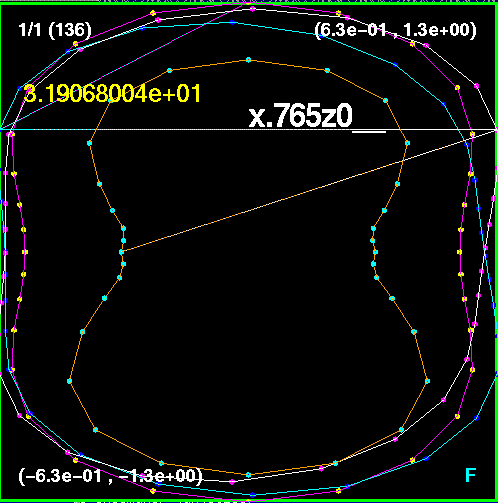
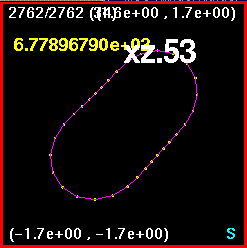
Separation of holes = 2.0, the need to break is detected as expected.
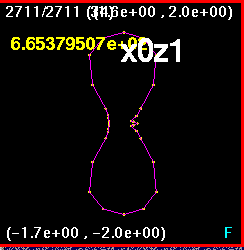
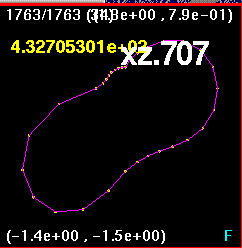
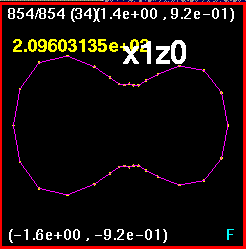
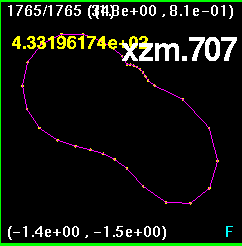
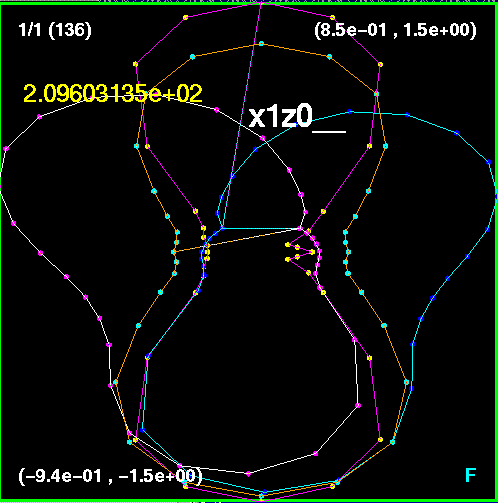
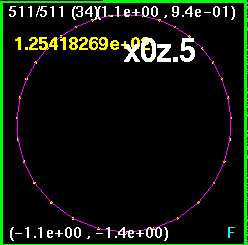
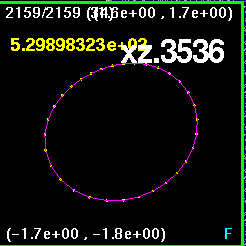
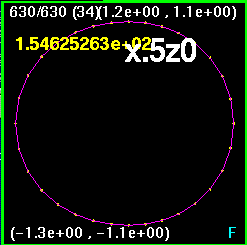
Now all four snapshots are orientated and merged together. The
lines are color coded such that
x0z1 is purple, xz.707 is white, xzm.707 is blue, and x1z0 is
orange. Here, the largest
discrepancy appears to be in the off-axis runs, the run (0.707,0.707)
and (-0.707,-0.707) and
the run (-0.707,0.707) and (0.707,-0.707).